Inhalt:
Nr.1
The redox potential as a way to determine the effect of disinfectants on the example of a Twin Oxide Process 1% Solution
Nr.2
Temperaturabhängigkeiten
Nr. 3
Elektrochemische Spannungsreihe
Nr.4
Beispiel aus einem Schwimmbadprojekt
Nr.1
The redox potential as a way to determine the effect of disinfectants on the example of a Twin Oxide Process 1% Solution
Dr. -Ing. Wolfgang Storch -2014-03-19
The redox potential is dissolved in the water oxidizing and reducing
The relationship between ORP and the concentration of the disinfectant is not linear.
In the waterworks practice, the redox potential as a measure of the disinfectant property offers particularly where such waters are treated , where at times, with a greater occurrence of organic pollutants , such as algenbürtigen substances or ammonium , must be expected . In these periods, the indication of the disinfectant concentration loses its significance , while the measurement of the redox potential allows an accurate statement about the still existing disinfection assets.
Another aspect arises out of the difficult analysis of chlorine and chlorine dioxide at very low concentrations . To lowest possible disinfectant levels to control , but to still ensure safe disinfection , the redox potential offers itself as an appropriate measure because they most responsive in very low concentration ranges to changes in the concentration of disinfectant .
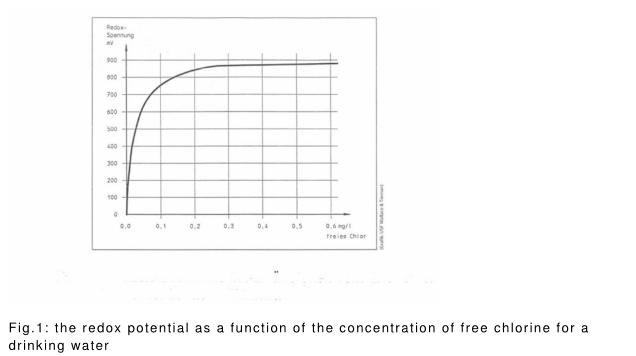
Figure 1 shows the redox potential with increasing content of free chlorine.
Limits or ranges for the redox potential required for safe disinfection , are nowhere defined.
To find out in a waterworks which redox potential for reliable disinfection is necessary trials are required. Here, the microbiological testing , the amount of disinfectant , and the pH value associated with the value of the redox potential should be seen .
In the alternative, may initially be determined as a function of the redox potential of the dose of disinfectant (twin Oxide 0, 3 % solution or twin Oxide Process Solution) for the water to be treated . This results in the dose range of the disinfectant. Microbiological tests with test bacteria can then follow .
In the picture part, the correlations are illustrated.
Although in DIN 38404 , Part 6 ( determining the redox potential ) , the redox potential as a tension between an inert electronic conductor and the standard hydrogen electrode is to be specified, for practical reasons, the measurement with a platinum electrode against a silver / silver chloride (Ag / AgCl) reference electrode performed.
On measuring module, the actual measured voltage UG ( vs. Ag / AgCl) is displayed.
Nr.1
The redox potential as a way to determine the effect of disinfectants on the example of a Twin Oxide Process 1% Solution
Nr.2
Temperaturabhängigkeiten
Nr. 3
Elektrochemische Spannungsreihe
Nr.4
Beispiel aus einem Schwimmbadprojekt
The redox potential as a way to determine the effect of disinfectants on the example of a Twin Oxide Process 1% Solution
Sources:
Die Desinfektionswirkung eines Stoffes, also auch von Chlordioxidgas, TwinOxide-Solutions,... ist vom Redoxpotential abhängig.
Die geringe Temperaturabhängigkeit des Redoxpotentials von Chlordioxid weist auf dessen hohe Temperaturstabilität der Desinfektion hin.
Nr.2 Temperaturabhängigkeiten
Die Desinfektionswirkung eines Stoffes, also auch von Chlordioxidgas, TwinOxide-Solutions,... ist vom Redoxpotential abhängig.
Die geringe Temperaturabhängigkeit des Redoxpotentials von Chlordioxid weist auf dessen hohe Temperaturstabilität der Desinfektion hin.
Nr.2 Temperaturabhängigkeiten
Nr. 3
Elektrochemische Spannungsreihe
nach: http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elektrochemische_SpannungsreiheThe electrochemical series is a collection of oxidants on the oxidation strength and at the same time a reverse listing of reducing agents by reducing strength.
In addition, the electrochemical series contains a gradation of metals ("very noble metal", "noble metal", "less noble metal", "ignoble metal", "very ignoble metal") to their quest to can be oxidized into acids. The standard potentials of the noble metals have a positive sign that the ignoble on the other hand a negative. The base metals therefore dissolve in acids because acids contain H +. (The arguments, for example, Zn / Cu analogously apply.)
Die elektrochemische Spannungsreihe ist damit eine Auflistung von Oxidationsmitteln nach Oxidationsstärke bzw. gleichzeitig eine umgekehrte Auflistung von Reduktionsmitteln nach Reduktionsstärke.
Außerdem enthält die elektrochemische Spannungsreihe eine Abstufung der Metalle („sehr edles Metall“, „edles Metall“, „weniger edles Metall“, „unedles Metall“, „sehr unedles Metall“) nach ihrem Bestreben, sich in Säuren oxidieren zu lassen. Die Standardpotentiale der edlen Metalle haben ein positives Vorzeichen, die der unedlen dagegen ein negatives. Die unedlen Metalle lösen sich daher in Säuren auf, weil Säuren H+ enthalten. (Die Argumente zum Beispiel Zn/Cu gelten analog.)
Elektrochemische Spannungsreihe
(Standardpotentiale bei 25 °C; 101,3 kPa; pH=0; Ionenaktivitäten= 1)
Element im Redox-Paar,
| ||||
dessen Oxidationsstufe
| ||||
sich ändert
|
oxidierte Form
|
+ z e−
|
⇌ reduzierte Form
|
Standardpotential E °
|
Fluor (F)
|
F2
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ 2 F−
|
+2,87 V
|
Sauerstoff (O)
|
S2O82−
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ 2 SO42−
|
+2,00 V
|
Sauerstoff (O)
|
H2O2 + 2 H3O+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ 4 H2O
|
+1,78 V
|
Gold (Au)
|
Au+
|
+ e−
|
⇌ Au
|
+1,69 V
|
Gold (Au)
|
Au3+
|
+ 3 e−
|
⇌ Au
|
+1,42 V
|
Gold (Au)
|
Au2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Au
|
+1,40 V
|
Chlor (Cl)
|
Cl2
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ 2 Cl−
|
+1,36 V
|
Chrom (Cr)
|
Cr6+
|
+ 3 e-
|
⇌ Cr3+
|
+1,33 V
|
Sauerstoff (O)
|
O2 + 4 H3O+
|
+ 4 e−
|
⇌ 6 H2O
|
+1,23 V
|
Platin (Pt)
|
Pt2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Pt
|
+1,20 V
|
Brom (Br)
|
Br2
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ 2 Br−
|
+1,07 V
|
Quecksilber (Hg)
|
Hg2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Hg
|
+0,85 V
|
Silber (Ag)
|
Ag+
|
+ e−
|
⇌ Ag
|
+0,80 V
|
Eisen (Fe)
|
Fe3+
|
+ e−
|
⇌ Fe2+
|
+0,77 V
|
Iod (I)
|
I2
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ 2 I−
|
+0,53 V
|
Kupfer (Cu)
|
Cu+
|
+ e−
|
⇌ Cu
|
+0,52 V
|
Eisen (Fe)
|
[Fe(CN)6]3−
|
+ e−
|
⇌ [Fe(CN)6]4−
|
+0,361 V
|
Kupfer (Cu)
|
Cu2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Cu
|
+0,35 V
|
Kupfer (Cu)
|
Cu2+
|
+ e−
|
⇌ Cu+
|
+0,16 V
|
Zinn (Sn)
|
Sn4+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Sn2+
|
+0,15 V
|
Wasserstoff (H2)
|
2 H+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ H2
|
0
|
Blei (Pb)
|
Pb2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Pb
|
−0,13 V
|
Zinn (Sn)
|
Sn2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Sn
|
−0,14 V
|
Molybdän (Mo)
|
Mo3+
|
+ 3 e−
|
⇌ Mo
|
−0,20 V
|
Nickel (Ni)
|
Ni2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Ni
|
−0,23 V
|
Cadmium (Cd)
|
Cd2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Cd
|
−0,40 V
|
Eisen (Fe)
|
Fe2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Fe
|
−0,44 V
|
Schwefel (S)
|
S
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ S2−
|
−0,48 V
|
Nickel (Ni)
|
NiO2 + 2 H2O
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Ni(OH)2 + 2 OH−
|
−0,49 V
|
Chrom (Cr)
|
Cr3+
|
+ 3 e−
|
⇌ Cr
| |
Zink (Zn)
|
Zn2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Zn
|
−0,76 V
|
Eisen (Fe)
|
Fe3+
|
+ 3 e−
|
⇌ Fe
|
−0,77 V
|
2 H2O
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ H2 + 2 OH−
|
−0,83 V
| |
Chrom (Cr)
|
Cr2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Cr
|
−0,91 V
|
Niob (Nb)
|
Nb3+
|
+ 3 e−
|
⇌ Nb
|
−1,099 V
|
Vanadium (V)
|
V2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ V
|
−1,17 V
|
Mangan (Mn)
|
Mn2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Mn
|
−1,18 V
|
Titan (Ti)
|
Ti3+
|
+ 3 e−
|
⇌ Ti
|
−1,21 V
|
Aluminium (Al)
|
Al3+
|
+ 3 e−
|
⇌ Al
|
−1,66 V
|
Titan (Ti)
|
Ti2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Ti
|
−1,77 V
|
Beryllium (Be)
|
Be2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Be
|
−1,85 V
|
Magnesium (Mg)
|
Mg2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Mg
|
−2,38 V
|
Cer (Ce)
|
Ce3+
|
+ 3 e−
|
⇌ Ce
|
−2,483 V
|
Lanthan (La)
|
La3+
|
+ 3 e−
|
⇌ La
|
−2,522 V
|
Natrium (Na)
|
Na+
|
+ e−
|
⇌ Na
|
−2,71 V
|
Calcium (Ca)
|
Ca2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Ca
|
−2,76 V
|
Barium (Ba)
|
Ba2+
|
+ 2 e−
|
⇌ Ba
|
−2,90 V
|
Kalium (K)
|
K+
|
+ e−
|
⇌ K
|
−2,92 V
|
Lithium (Li)
|
Li+
|
+ e−
|
⇌ Li
|
−3,05 V
|
Merkspruch für die Spannungsreihe ausgewählter Elemente [Bearbeiten]
Kaiser Napoleon mag alle zackigen Soldaten - Blei haben cubanische Agenten auch (K - Na - Mg - Al - Zn - Sn - Pb - H - Cu - Ag - Au)
Literatur [Bearbeiten]
- Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC press, 1995 Electrochemical Series
- Anorganische Chemie, Buchners Verlag, 1972
- Elemente Chemie II, Klett Verlag, 2000
Nr. 4
Beispiel aus einem Schwimmbadprojekt













No comments:
Post a Comment